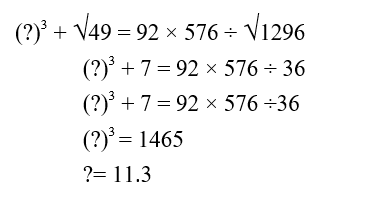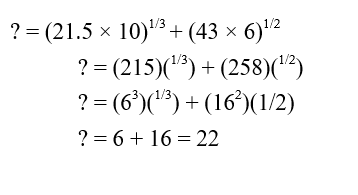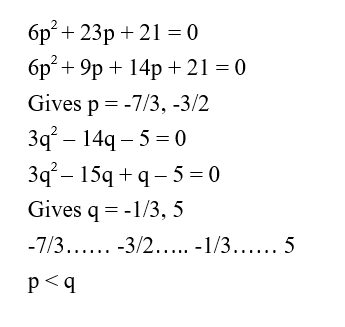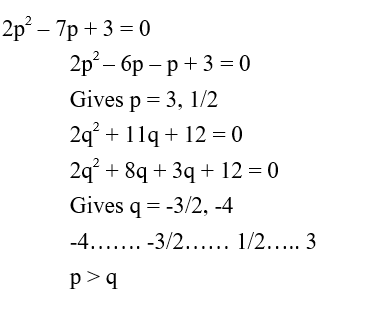Question 1:
निर्देश : निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों में प्रश्न चिह्न (?) के स्थान पर अनुमानित मान क्या होना चाहिए?
Direction : What approximate value should come in place of question mark (?) in the following questions?
4.01× 4.001 × 4.999 × 4.999 = 4 × ?
Question 2:
निर्देश : निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों में प्रश्न चिह्न (?) के स्थान पर अनुमानित मान क्या होना चाहिए?
Direction : What approximate value should come in place of question mark (?) in the following questions?
299.011 ÷ 12 × 13.95 + ? = (23.98)2
Question 3:
निर्देश : निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों में प्रश्न चिह्न (?) के स्थान पर अनुमानित मान क्या होना चाहिए?
Direction : What approximate value should come in place of question mark (?) in the following questions?
92.01 × 576.012 ÷ √1296.01 = (?)3 + √49
Question 4:
निर्देश : निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों में प्रश्न चिह्न (?) के स्थान पर अनुमानित मान क्या होना चाहिए?
Direction : What approximate value should come in place of question mark (?) in the following questions?
(21.51% of 999.01) (1/3) + (43% of 601.1)1/2 = ?
Question 5:
निर्देश : निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों में प्रश्न चिह्न (?) के स्थान पर अनुमानित मान क्या होना चाहिए?
Direction : What approximate value should come in place of question mark (?) in the following questions?
900.011÷45.072= ?– 224.488
Question 6: 
Question 7: 
Question 8: 
Question 9: 
Question 10: