Question 1:
Direction : Answer the questions based on the information given below.
निर्देश : नीचे दी गई जानकारी के आधार पर प्रश्नों के उत्तर दें।
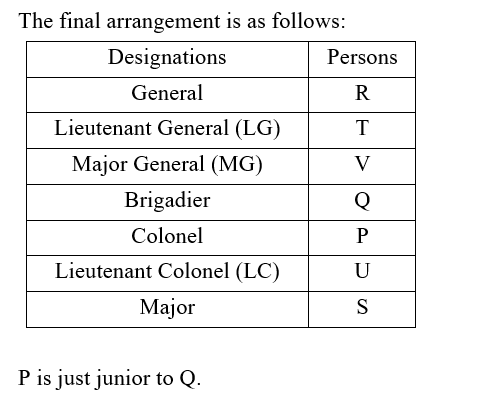
Seven people P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V posted in seven different ranks in the Indian Army i.e., General, Lieutenant General (LG), Major General (MG), Brigadier, Colonel, Lieutenant Colonel (LC) and Major but not in the same order. Also, ranks are given in descending order such that General being the senior-most post and Major being the junior-most post among the given posts of Indian Army.
Note: If it is given that X is senior to Y then it means X ranks in a higher post than Y.
R is senior to the one, who is the Brigadier. More than two designations are there between R and P, who is not LC. There is only one person in the hierarchy between P and S. Number of people designated between R and Q is same as the number of people designated between Q and S. U is junior to V. Q is not the LG. Only one person is designated between Q and T, who is senior to V.
सात लोग P, Q, R, S, T, U, और V भारतीय सेना में सात अलग-अलग रैंकों में तैनात हैं अर्थात जनरल, लेफ्टिनेंट जनरल (LG), मेजर जनरल (MG), ब्रिगेडियर, कर्नल, लेफ्टिनेंट कर्नल (LC) और मेजर लेकिन ये आवश्यक नहीं कि समान क्रम में इसके अलावा, रैंक अवरोही क्रम में दी गई हैं जहाँ भारतीय सेना में दिए गए पदों में से जनरल सबसे वरिष्ठ पद है और मेजर सबसे कनिष्ठ पद है।
ध्यान दें:
यदि यह ज्ञात है कि X, Y से वरिष्ठ है तो इसका अर्थ है कि X, Y से उच्च पद पर है।
R उस व्यक्ति से वरिष्ठ है, जो ब्रिगेडियर है। R और P के बीच दो से अधिक पद हैं और P, LC नहीं है। P और S के बीच पदानुक्रम में केवल एक व्यक्ति है। R और Q के बीच पदानुक्रम में व्यक्तियों की संख्या और Q और S के बीच पदानुक्रम में व्यक्तियों की संख्या समान है। U, V से कनिष्ठ है। Q, LG नहीं है। Q और T जो V से वरिष्ठ है, के बीच केवल एक व्यक्ति को नामित किया गया है।
Who among the following is just junior to Q?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन Q से तत्काल कनिष्ठ है?
Question 2:
Direction : Answer the questions based on the information given below.
निर्देश : नीचे दी गई जानकारी के आधार पर प्रश्नों के उत्तर दें।
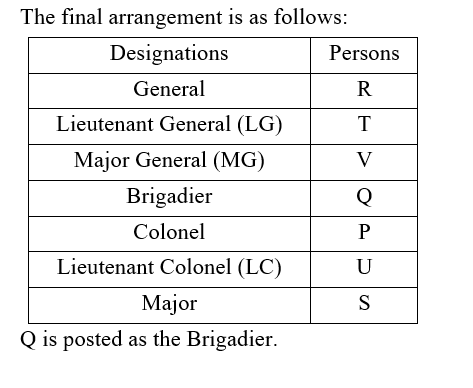
Seven people P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V posted in seven different ranks in the Indian Army i.e., General, Lieutenant General (LG), Major General (MG), Brigadier, Colonel, Lieutenant Colonel (LC) and Major but not in the same order. Also, ranks are given in descending order such that General being the senior-most post and Major being the junior-most post among the given posts of Indian Army.
Note: If it is given that X is senior to Y then it means X ranks in a higher post than Y.
R is senior to the one, who is the Brigadier. More than two designations are there between R and P, who is not LC. There is only one person in the hierarchy between P and S. Number of people designated between R and Q is same as the number of people designated between Q and S. U is junior to V. Q is not the LG. Only one person is designated between Q and T, who is senior to V.
सात लोग P, Q, R, S, T, U, और V भारतीय सेना में सात अलग-अलग रैंकों में तैनात हैं अर्थात जनरल, लेफ्टिनेंट जनरल (LG), मेजर जनरल (MG), ब्रिगेडियर, कर्नल, लेफ्टिनेंट कर्नल (LC) और मेजर लेकिन ये आवश्यक नहीं कि समान क्रम में इसके अलावा, रैंक अवरोही क्रम में दी गई हैं जहाँ भारतीय सेना में दिए गए पदों में से जनरल सबसे वरिष्ठ पद है और मेजर सबसे कनिष्ठ पद है।
ध्यान दें:
यदि यह ज्ञात है कि X, Y से वरिष्ठ है तो इसका अर्थ है कि X, Y से उच्च पद पर है।
R उस व्यक्ति से वरिष्ठ है, जो ब्रिगेडियर है। R और P के बीच दो से अधिक पद हैं और P, LC नहीं है। P और S के बीच पदानुक्रम में केवल एक व्यक्ति है। R और Q के बीच पदानुक्रम में व्यक्तियों की संख्या और Q और S के बीच पदानुक्रम में व्यक्तियों की संख्या समान है। U, V से कनिष्ठ है। Q, LG नहीं है। Q और T जो V से वरिष्ठ है, के बीच केवल एक व्यक्ति को नामित किया गया है।
Who is posted as the Brigadier?
ब्रिगेडियर के पद पर कौन तैनात है?
Question 3:
Rakesh, Rinki and Rakhi start a business by investing ₹33120, ₹x and ₹36800, respectively. At the end of year, profit share of Rinki is 20% less than the profit share of Rakhi and profit share of Rakesh is equal to the average profit of Rinki and Rakhi. If at the end of year, profit share of Rakhi is ₹920 then find the value of ‘x’.
राकेश, रिंकी और राखी ने क्रमशः 33120, रु.x और रु.36800 का निवेश करके एक व्यवसाय शुरू करते हैं। वर्ष के अंत में, रिंकी का लाभ हिस्सा राखी के लाभ हिस्से से 20% कम है और राकेश का लाभ हिस्सा रिंकी और राखी के लाभ के औसत के बराबर है। यदि वर्ष के अंत में, राखी का लाभ हिस्सा रु.920 है तो 'x' का मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
Question 4:
After 4 years, ratio of age of ‘A’ to ‘B’ will be 2:3 respectively. Age of ‘B’, 2 years ago was 80% more than age of ‘A’, 6 years ago. If present average age of ‘B’ and ‘C’ is 48 years, then find ratio of present age of ‘A’ to ‘C’.
4 वर्ष बाद, 'A' की आयु और 'B' की आयु का अनुपात क्रमशः 2:3 होगा। 2 वर्ष पहले 'B' की आयु, 6 वर्ष पहले 'A' की आयु से 80% अधिक थी। यदि 'B' और 'C' की वर्तमान औसत आयु 48 वर्ष है, तो 'A' और 'C' की वर्तमान आयु का अनुपात ज्ञात कीजिए।
Question 5:
In a test, 40% students failed in Science, 44% students failed in Sanskrit and 24% of students failed in both the subjects. If the number of students who passed in both the subjects is 480, then find total number of students who appeared for the test.
एक परीक्षा में, 40% छात्र विज्ञान में अनुत्तीर्ण हुए, 44% छात्र संस्कृत में अनुत्तीर्ण हुए और 24% छात्र दोनों विषयों में अनुत्तीर्ण हुए। यदि दोनों विषयों में उत्तीर्ण होने वाले छात्रों की संख्या 480 है, तो परीक्षा में बैठने वाले छात्रों की कुल संख्या ज्ञात कीजिए।
Question 6:
Article ‘A’ whose cost price is ₹(x + 400) is sold at 25% profit such the profit received is ₹(0.75x – 500). Find the selling price of article ‘B’ whose cost price is ₹(2x + 800) and which is sold at 25% loss.
वस्तु 'A' जिसका क्रय मूल्य ₹(x + 400) को 25% लाभ पर बेचा जाता है और प्राप्त लाभ ₹(0.75x – 500) है। वस्तु 'B' का विक्रय मूल्य ज्ञात कीजिए जिसका क्रय मूल्य ₹(2x + 800) है और जिसे 25% हानि पर बेचा जाता है।
Question 7:
₹12800 invested at a certain rate p.a. compounded annually amounts to ₹16200 at the end of 2 years. Find the rate of interest.
₹12800 को वार्षिक देय चक्रवृद्धि ब्याज की कुछ दर पर निवेश किया जाता है और यह दो वर्ष के अंत में सयंचित होकर ₹16200 हो जाती है| ब्याज दर ज्ञात कीजिए।
Question 8:
The ratio of water to alcohol in mixture ‘A’ is 5:4. Mixture ‘B’ contains 23 litre water and 48 litre alcohol. If mixtures ‘A’ and ‘B’ is mixed in a empty beaker and ratio of alcohol to water in the beaker becomes 17:12, then find the quantity of water in mixture ‘A’.
मिश्रण 'A' में पानी और अल्कोहल का अनुपात 5:4 है। मिश्रण 'B' में 23 लीटर पानी और 48 लीटर अल्कोहल है। यदि मिश्रण ‘A’ और ‘B’ को एक खाली बीकर में मिलाया जाता है और बीकर में अल्कोहल और पानी का अनुपात 17:12 हो जाता है, तो मिश्रण 'A' में पानी की मात्रा ज्ञात कीजिए।
Question 9:
The speed of a boat in still water is 32 km/hr which is 60% more than the speed of the current. If the boat can travel (x + 80) km downstream in 5 hours, then find the time taken by the boat to travel (x – 84) km upstream.
शांत जल में एक नाव की गति 32 किमी/घंटा है जो धारा की गति से 60% अधिक है। यदि नाव धारा अनुप्रवाह में (x + 80) किमी की दूरी को तय करने में 5 घंटे लगा सकती है, तो नाव द्वारा धारा विरुद्ध में (x – 84) किमी की दूरो को तय करने में लगने वाला समय ज्ञात कीजिए।
Question 10:
304 ml of mixture contains milk and water in the ratio of 12:7, respectively. Find the quantity of water that must be added into the mixture so that ratio of milk to water changes to 6:5.
304 मिली मिश्रण में दूध और पानी क्रमशः 12:7 के अनुपात में हैं। मिश्रण में पानी की कितनी मात्रा मिलाने पर मिश्रण में दूध और पानी का अनुपात 6:5 हो जाए।